通常情况下,一个activity可能包含一个或多个fragment,它们协同工作,组成一个连贯的UI界面。在这种情况下,多个fragments之间的通信显得就很重要了。举个例子,一个activity包含左右两个fragment,左侧的fragment包含了一个列表(比如新闻题目列表),当点击每个新闻题目的时候,右侧的fragment就会显示这条新闻的详尽信息。
下面展示如何进行操作。
工程目录:
Fragment1在整个activity的左侧,Fragment2在右侧。
1.fragment1.xml中的代码。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:
Android="http://schemas.
Android.com/apk/res/
Android"
Android:layout_width="fill_parent"
Android:layout_height="fill_parent"
Android:background="#00FF00"
Android:orientation="vertical" >
<TextView
Android:id="@+id/lblFragment1"
Android:layout_width="fill_parent"
Android:layout_height="wrap_content"
Android:text="This is fragment #1"
Android:textColor="#000000"
Android:textSize="25sp" />
</LinearLayout>
2.fragment2.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:
Android="http://schemas.
Android.com/apk/res/
Android"
Android:layout_width="fill_parent"
Android:layout_height="fill_parent"
Android:background="#FFFE00"
Android:orientation="vertical" >
<TextView
Android:layout_width="fill_parent"
Android:layout_height="wrap_content"
Android:text="This is fragment #2"
Android:textColor="#000000"
Android:textSize="25sp" />
<Button
Android:id="@+id/btnGetText"
Android:layout_width="wrap_content"
Android:layout_height="wrap_content"
Android:onClick="onClick"
Android:text="Get text in Fragment #1"
Android:textColor="#000000" />
</LinearLayout>
3.main.xml中的代码。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:
Android="http://schemas.
Android.com/apk/res/
Android"
Android:layout_width="fill_parent"
Android:layout_height="fill_parent"
Android:orientation="horizontal" >
<fragment
Android:id="@+id/fragment1"
Android:name="net.learn2develop.Fragments.Fragment1"
Android:layout_width="0px"
Android:layout_height="match_parent"
Android:layout_weight="1" />
<fragment
Android:id="@+id/fragment2"
Android:name="net.learn2develop.Fragments.Fragment2"
Android:layout_width="0px"
Android:layout_height="match_parent"
Android:layout_weight="1" />
</LinearLayout>
4.FragmentsActivity.
java中的代码。
package net.learn2develop.Fragments;
import
Android.app.Activity;
import
Android.os.Bundle;
import
Android.view.View;
import
Android.widget.TextView;
import
Android.widget.Toast;
public class FragmentsActivity extends Activity {
/** Called when the activity is first created. */
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
}
public void onClick(View v) {
TextView lbl = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.lblFragment1);
Toast.makeText(this, lbl.getText(), Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
}
5.Fragment2.
java中的代码。
package net.learn2develop.Fragments;
import
Android.app.Fragment;
import
Android.os.Bundle;
import
Android.view.LayoutInflater;
import
Android.view.View;
import
Android.view.ViewGroup;
import
Android.widget.Button;
import
Android.widget.TextView;
import
Android.widget.Toast;
public class Fragment2 extends Fragment {
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container,
Bundle savedInstanceState) {
// ---Inflate the layout for this fragment---
return inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment2, container, false);
}
@Override
public void onStart() {
super.onStart();
// ---Button view---
Button btnGetText = (Button) getActivity()
.findViewById(R.id.btnGetText);
btnGetText.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
public void onClick(View v) {
// 这里是关键,getActivity()方法返回这个fragment所在的activity实例,通过activity实例可以获取在其中的组件,其他就很简单了。
www.atcpu.com TextView lbl = (TextView) getActivity().findViewById(
R.id.lblFragment1);
Toast.makeText(getActivity(), lbl.getText(), Toast.LENGTH_SHORT)
.show();
}
});
}
}
6.调试。效果图:
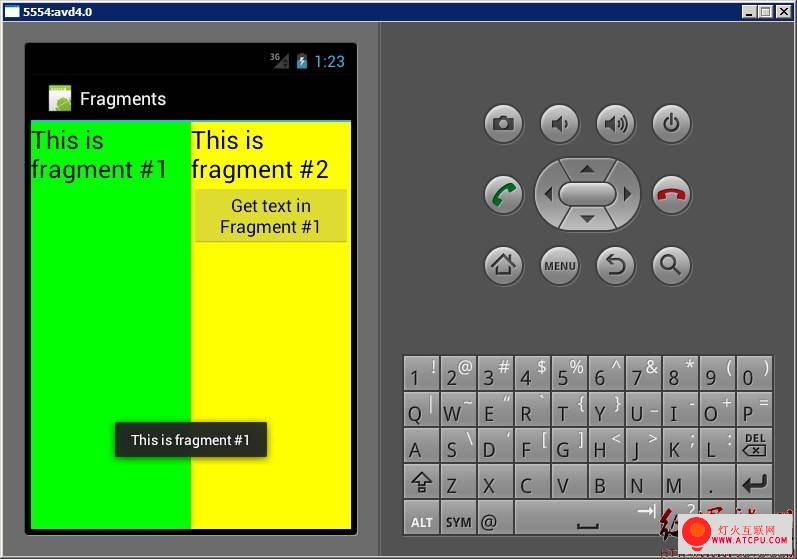
点击右边的“Get text in Fragment #1”按钮,将弹出一个提示。
摘自 manoel的专栏